The Ultimate Generative AI Crash Course: A Complete Guide
ToxSec | The only Generative AI guide you'll ever need. This comprehensive crash course covers what GenAI is, how LLMs work, prompt engineering, AI ethics, top tools, and the future of AI.
Introduction
You’ve seen the headlines and used the tools. Generative AI is a major technological shift, and this guide is your complete roadmap. This practical crash course is for professionals, creators, and anyone curious about this technology. We’ll break down how it works and give you the skills to use AI effectively.
Chapter 1: What is Generative AI (And Why Should You Care)?
Welcome to the starting line. Before diving in, let’s master the basics. The term “Generative AI” is everywhere, but what does it really mean? This chapter provides a solid foundation, moving beyond the hype to explain what this technology is, what makes it unique, and why it’s a huge shift in how we work and create.
Generative AI Defined in Plain English
At its core, Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates new, original content. Unlike other kinds of AI that might analyze or sort existing data, generative models produce something entirely new.
A search engine, for example, finds and shows you existing information. A Generative AI can take a concept and write a new poem, compose a unique piece of music, or design a logo that has never existed before. It creates new content rather than just finding existing information.
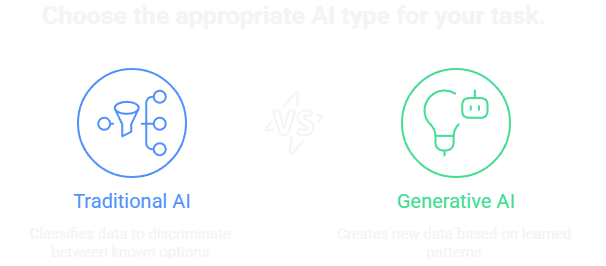
How is Generative AI Different from Traditional AI?
To understand this better, let’s compare Generative AI with its more traditional counterpart, often called Discriminative AI.
Imagine you’re training an AI to recognize cats and dogs.
A Traditional (Discriminative) AI learns to classify data. You show it a picture, and its job is to decide if it’s a “cat” or a “dog.” It discriminates between known options. Your email’s spam filter is a perfect example—it decides if an email is “spam” or “not spam.”
A Generative AI, in contrast, learns the underlying patterns in data so it can create new examples. You give it a description like, “a photorealistic image of a fluffy golden retriever puppy sleeping in a sunbeam.” The AI then creates a new image from scratch. It doesn’t just classify; it originates.
What Can Generative AI Actually Do? (Key Capabilities)
People are already using GenAI to transform industries. Here are a few of the core things that make this technology so powerful:
Content Creation: This is the most famous use case. It can write blog posts, marketing copy, social media updates, and even entire screenplays. It’s a powerful assistant for overcoming writer’s block.
Summarization and Synthesis: Generative AI can read a 50-page report or a long email thread and boil it down to a few key bullet points, saving hours of work.
Code Generation: For developers, AI is a game-changer. It can write boilerplate code, debug functions, and explain what a snippet of code does in plain English.
Creative Ideation & Brainstorming: Stuck for an idea? Ask an AI to brainstorm marketing slogans, come up with plot ideas for a novel, or suggest names for a new podcast.
Enjoying the guide? Share it with someone you think would it would benefit!
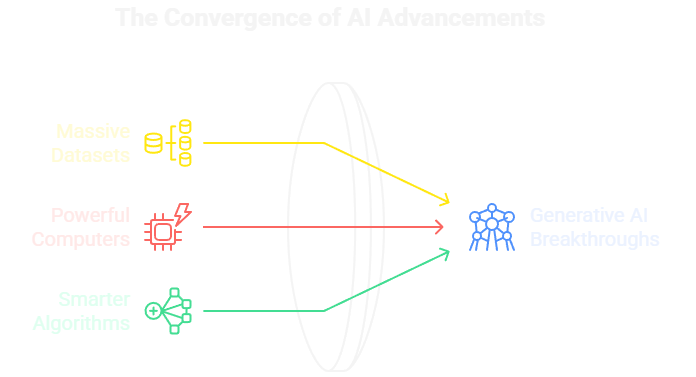
Why is Generative AI Exploding Right Now?
AI isn’t new, so why is this happening now? It’s the result of three key factors coming together:
Massive Datasets: These models are trained on an incredible amount of data from the public internet. This vast library gives them a deep understanding of language, context, and concepts.
Powerful Computers: Training these huge models requires immense processing power. Modern hardware, like GPUs, has made it possible to process this data at a scale that was unimaginable a decade ago.
Smarter Algorithms: Breakthroughs in model design, especially the “Transformer architecture,” allowed models to understand how words in a sentence relate to each other far more effectively.
Now you understand the ‘what’ and ‘why.’ In Chapter 2, we’ll explore the technology that makes it all possible.
Chapter 2: How Does Generative AI Work?
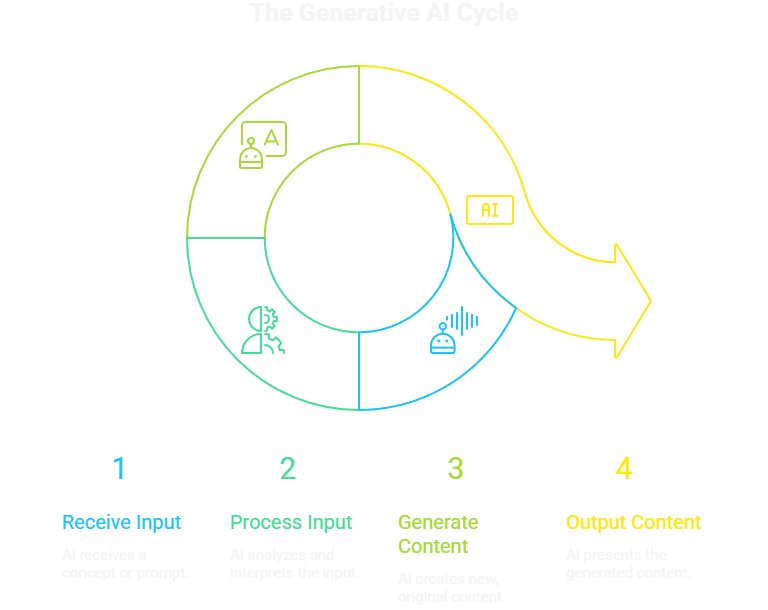
If Chapter 1 was about what GenAI does, this chapter is about how. How can a machine write a poem or create a photorealistic image? The process is a combination of clever math and huge scale.
How Do Large Language Models (LLMs) Work?
The engine behind text-based AI is the Large Language Model (LLM). At its core, an LLM is a sophisticated prediction machine. Its main goal is surprisingly simple: to predict the next most likely word in a sentence.
When you type “The sky is,” your brain instantly thinks “blue.” An LLM does the same thing on a massive scale. It has analyzed trillions of words from books, articles, and websites. From that data, it has learned that, statistically, the word “blue” is the most probable word to follow “The sky is.” It then chains these predictions together to form coherent sentences and paragraphs.
The Secret Sauce: What is the Transformer Architecture?
For years, predicting the next word was difficult because of context. In the sentence, “The driver handed the package to the customer, and he seemed happy,” an older AI might not know if “he” refers to the driver or the customer.
The big breakthrough was the Transformer architecture, introduced in 2017. Its key feature is “self-attention,” which allows the model to weigh the importance of all the different words in a text to understand their relationships, no matter how far apart they are. This ability to track context is why modern AI conversations feel so natural.
How Do AI Image Generators Work?
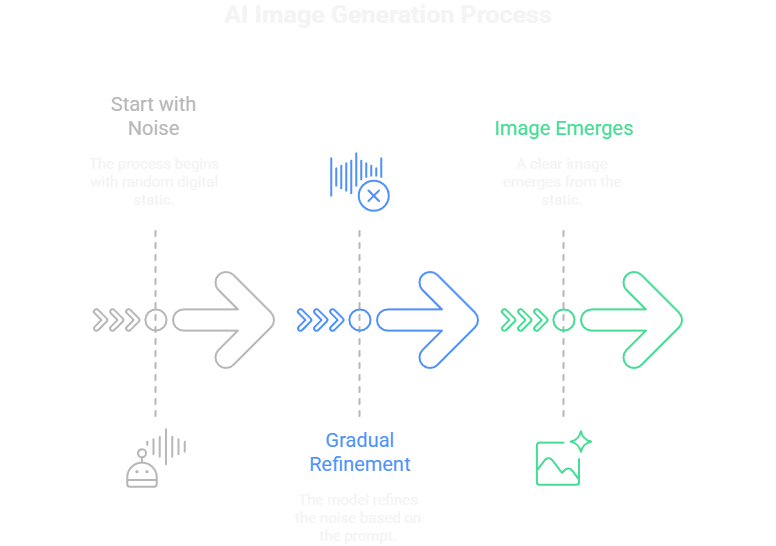
Image generators like Midjourney and DALL-E work on a different but equally cool principle called diffusion.
Imagine the process in reverse:
Start with Noise: The model begins with a canvas full of random digital static.
Gradual Refinement: Guided by your text prompt (e.g., “an astronaut riding a horse on Mars”), the model slowly starts to remove the noise, step-by-step.
An Image Emerges: With each step, it refines the noise to more closely match the concepts in your prompt until a clear image emerges from the static.
Be sure to subscribe to ToxSec to keep getting AI and cybersecurity related content straight to your inbox.
How is an AI Model Trained?
Whether for text or images, these models go through a tough, two-part training process:
Pre-training: This is the general education phase. The model learns the patterns, grammar, and relationships from a colossal dataset on its own.
Fine-Tuning: After its broad education, the model is specialized for a specific task, like being a helpful chatbot. This often involves humans reviewing and ranking the AI’s responses to teach it what a “good” answer looks like.
Knowing the theory is great, but the real power comes from using it. In Chapter 3, you’ll learn the crucial skill of prompt engineering.
Chapter 3: What is Prompt Engineering? A Guide to Talking to AI
You understand what GenAI is and how it works. Now for the most important part: making it work for you. The most critical skill for getting value from Generative AI is prompt engineering—writing clear instructions to get the best possible results.
Why is Good Prompting a Superpower?
Think of yourself as a film director and the AI as an actor. Vague instructions lead to a generic performance. Specific, detailed direction leads to a great one. It’s the same with AI. A vague prompt gets you a useless response. A clear, well-structured prompt unlocks the AI’s full potential.
The Core Components of a Perfect Prompt
Effective prompts rely on structure. You won’t need all of these every time, but knowing them will dramatically improve your results.
Role & Persona: Tell the AI who it should be. This sets the tone and style.
Example: “Act as a senior marketing copywriter.”
Task & Action: Be explicit about what you want it to do.
Example: “Write three compelling Facebook ad headlines.”
Context & Constraints: Give it the background info and the rules.
Example: “...for a new brand of sustainable coffee. The target audience is millennials. The headlines must be under 12 words and include an emoji.”
Format & Tone: Tell it how you want the output to look.
Example: “Put the output in a markdown table. The tone should be witty and energetic.”
Putting it all together, a weak prompt like “write coffee ads” becomes a powerful prompt like:
“Act as a senior marketing copywriter. Write three compelling Facebook ad headlines for a new brand of sustainable coffee. The target audience is millennials. The headlines must be under 12 words and include an emoji. Put the output in a markdown table. The tone should be witty and energetic.”
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
Being Too Vague: “Write a blog post about AI” is a recipe for a generic article.
Not Providing Context: If you don’t tell the AI who your audience is, it can’t tailor the message.
Giving Up After One Try: Think of it like a conversation. Tweak your instructions, ask for changes, and keep refining until you get what you want.
You’re now ready to be an AI power user. In Chapter 4, we’ll explore the most popular GenAI tools and their real-world uses.
Chapter 4: The Top Generative AI Tools and Use Cases
Now that you can “speak AI,” it’s time to choose your tools. The AI world is full of new platforms, each with its own strengths. The key is to find the best tool for your specific task.
The Best AI Text and Chatbot Tools
Google’s Gemini: A powerhouse known for its deep integration with the Google ecosystem and its native ability to understand text, images, code, and video.
OpenAI’s GPT series (ChatGPT): The model that made GenAI famous. It’s loved for its creative writing skills, strong conversational abilities, and a huge ecosystem of plugins.
Anthropic’s Claude: A strong competitor known for its ability to analyze very long documents and its focus on AI safety and producing reliable outputs.
The Best AI Image Generation Tools
Midjourney: The leader in artistic and highly stylized images. It’s known for producing beautiful, cinematic, and often surreal visuals.
DALL-E 3: Integrated into ChatGPT, it excels at following complex prompts accurately, making it great for specific design mockups.
Stable Diffusion: The open-source champion. It offers incredible control and customizability, making it a favorite for developers and advanced users.
How is Generative AI Used in Business?
Marketing: Generating ad copy, drafting SEO-optimized blog outlines, and creating social media content calendars.
Sales: Summarizing customer calls, drafting personalized follow-up emails, and doing quick research on prospects.
Software Development: Writing tests for code, explaining complex codebases to new developers, and prototyping new features.
Customer Support: Powering smart chatbots, summarizing support tickets, and drafting helpful replies.
The possibilities are endless. In Chapter 5, we’ll tackle the important topics of AI ethics, bias, and limitations.
Chapter 5: Understanding AI Ethics, Risks, and Limitations
Generative AI is a powerful tool, but it has limitations. Like any big new technology, it comes with risks and rules you need to know. Using AI effectively means understanding its limits and being aware of the questions it raises.
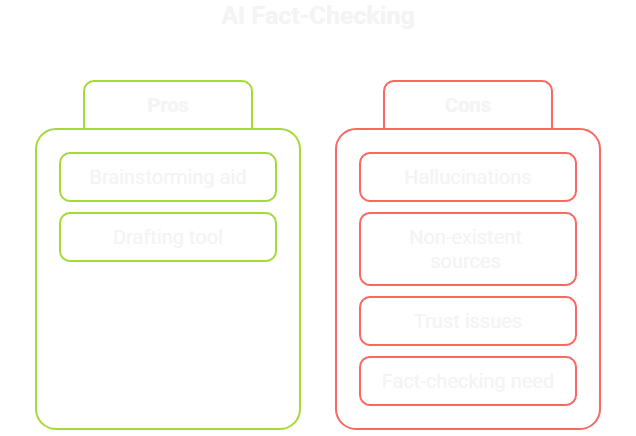
The “Hallucination” Problem: Can AI Make Things Up?
Yes. LLMs are not fact databases; they are word-prediction engines. This can lead to “hallucinations,” where an AI generates text that sounds plausible but is completely false. It might invent historical events or cite non-existent academic papers.
Why it matters: Blindly trusting AI for facts is a big mistake. How to handle it: Use AI for brainstorming and drafting, but always fact-check any specific claims or stats against reliable sources.
How Do You Prevent Bias in Generative AI?
AI models learn from the data we give them—and the internet is full of human bias. A model trained on this data can accidentally learn and then amplify harmful stereotypes related to gender, race, and culture.
Why it matters: If not managed, AI bias can make social inequalities even worse. How to handle it: Be aware of the potential for bias. Scrutinize the results for stereotypes. When prompting, be specific and inclusive (e.g., instead of “a photo of a leader,” try “a photo of a diverse team of leaders”).
Are There Copyright and Privacy Risks with AI?
Yes. GenAI has created a complex legal and ethical puzzle.
Copyright: Who owns an AI-generated image? The user, the AI company, or the public? The law is still catching up, and the answer varies.
Data Privacy: What happens to the information you type into a public AI tool? Assume your conversations can be used for training unless you use a business plan with data privacy guarantees.
How to handle it: Never input confidential company information or personal data into a public AI chatbot. Be mindful of your organization’s policies on AI use.
Understanding these risks is key to using AI responsibly. In our final chapter, Chapter 6, we’ll explore the exciting future of this technology.
Chapter 6: The Future of Generative AI
We’ve covered what GenAI is, how it works, and how to use it. But the technology is just beginning to develop and is moving incredibly fast. So, where is this all heading, and how can you stay prepared?
The Rise of Multimodality: An AI That Sees, Hears, and Speaks
The first AI tools were mostly single-taskers. The future is multimodal. This means single AI models will be able to understand and generate content across different formats—text, images, audio, and video. Imagine pointing your phone at a flat-pack furniture box, and an AI generates a custom video showing you exactly how to assemble it.
The Era of AI Agents: Your Own AI Teammate
Today, we use AI by giving it specific commands. The next big thing will be AI agents: systems that can take on complex, multi-step goals and work on them for you. Instead of asking an AI to “find flights to Tokyo,” you’ll give it a goal like, “Plan a five-day trip to Tokyo next month. Book the best flights and hotel, add it to my calendar, and suggest an itinerary.” This will transform AI from a tool you use into a teammate that works for you.
How to Stay Ahead in the AI Era
When tech moves this fast, keeping up can feel like a lot. The key is to be a continuous learner.
Be a Curator: Find a few trusted sources—researchers, newsletters, or tech journalists—and follow them consistently.
Be a Tinkerer: The best way to learn is by doing. Spend an hour each week experimenting with a new AI tool or prompting technique.
Focus on Your Human Skills: As AI automates routine tasks, human skills like strategic thinking, creative problem-solving, and leadership become more valuable than ever.
Conclusion
You’ve made it. From the basics of LLMs to the future of AI agents, you now have a solid foundation in Generative AI. We’ve broken down how it works, armed you with the skill of prompt engineering, and covered the essential ethical considerations.
The takeaway is this: Generative AI is one of the most powerful tools available today, and it’s here to stay. Your ability to understand it and use it skillfully will be a huge advantage. Use it as a co-pilot to boost your creativity and productivity to new heights.
Leave your thoughts, comments and questions below!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between Generative AI and regular AI? The main difference is creation vs. classification. Regular (or Discriminative) AI is designed to classify or analyze existing data (e.g., a spam filter). Generative AI is designed to create new, original content (e.g., writing an email or creating an image).
2. Is Generative AI free to use? Many powerful Generative AI tools, like Google’s Gemini and ChatGPT, offer free versions that are excellent for most users. They also offer paid subscription plans with access to more advanced models and features.
3. Can AI-generated content be detected? Sometimes. While many tools exist to detect AI-generated content, none are 100% accurate. As models become more sophisticated, detection becomes more difficult.
4. Will Generative AI take my job? Generative AI is more likely to change jobs rather than eliminate them entirely. It will act as a powerful “co-pilot,” automating repetitive tasks and freeing up professionals to focus on strategy, creativity, and complex problem-solving.






Good one
Thx for writing this!